BIC
Bank Identifier Code. code allocated to a financial institution by a Registration Authority
The following is the description of BIC in ISO20022 Payments Maintenance 2009 document:
Definition: Bank Identifier Code. code allocated to a financial institution by a Registration Authority
under an international identification scheme, as described in the latest edition of the international standard ISO 9362 "Banking - Banking telecommunication messages - Bank identifier codes".
Format: [A-Z]{6,6}[A-Z2-9][A-NP-Z0-9]([A-Z0-9]{3,3}){0,1}
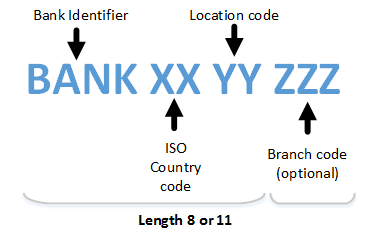
Rule(s): Valid BICs are registered with the ISO 9362 Registration Authority, and consist of eight (8) or eleven (11) contiguous characters comprising the first three or all four of the following components: BANK CODE, COUNTRY CODE, LOCATION CODE, BRANCH CODE.
The bank code, country code and location code are mandatory, while the branch code is
optional.
Example: CHASUS33
ISO 9362 Registration Authority does not have a list of registered BICs freely available so we cannot check whether certain BIC is associated with the registration authority. However, at minimum, we can check the format and the country code.
